Materials in flexible packaging
In the future, especially in France, flexible packaging is here to stay. With the explosion of e-commerce and environmental issues, this is the subject of much debate. Consumers are increasingly turning to online shopping for food, cosmetics, and household appliances. They also favour environmentally-friendly packaging design, sustainable materials, recycling... In short, for companies, flexible packaging design is a real challenge. And to meet consumers' new expectations, the most important choice is the materials used.
Polymer, paper, cardboard, aluminium... What are the roles, advantages, and disadvantages of these materials? Which ones should you choose for your products? We take a look at the materials used in flexible packaging.
Materials used in flexible packaging
Do you think you'll interest potential consumers with an original packaging design? It will undoubtedly attract their attention, but it's the material above all that will convince them. So when should you switch to environmentally-friendly design? When should you stick with polymer? Here is a list of the main materials used in flexible packaging in France today.Polymer
Although companies are being encouraged to reduce their consumption of polymer packaging, it is still the most widespread material in the world of flexible packaging. The reason for this? It meets all the requirements for preserving a solid, liquid, or pasty product. With polymer packaging, you can protect your product from the outside environment, preserve its quality over time, make transport easier and guarantee a good marketing presentation. But this ultra-versatile material is the subject of many questions, particularly when it comes to recyclability.
Here are the polymer materials you can use in flexible packaging
que vous pouvez utiliser dans le conditionnement d’emballages souples :
- Polymers that account for 90% of polymer packaging are known as: PE, PE, PP.
- Recycled polymers: reserved for certain applications, such as recycled PET for bottles or recycled HDPE for bin liners
- Biosourced polymers: derived from plant biomass, they are mainly used in the manufacture of bags, replacing non-recyclable single-use polymer bags
Aluminium
Aluminium may not be the most obvious material, but it is an integral part of our everyday lives. Yoghurt lids, medicine packets, coffee capsules, biscuit packaging... Aluminium is usually combined with other materials. It hides inside cardboard boxes or is stuck to paper packaging. This material is often the layer in direct contact with the product to be preserved, particularly for its ability to preserve food and pharmaceutical products. This includes its resistance to corrosion, light, humidity, oxygen, and micro-organisms. What's more, aluminium is one of the light, recyclable materials that can be used for both rigid and flexible packaging.
Cardboard and paper
Paper and cardboard are real environmentally-friendly design issues and play a key role in the circular economy in France. Because they are biodegradable, they constitute a raw material in their own right, which is a significant marketing advantage.
Barrier materials in packaging
Most packaging is made up of several films of different materials, which are bonded together to meet a specific need. This is known as multi-layer packaging. If the product requires a particular level of protection, barrier materials are added to these films.What is a barrier material ?
Before being practical and aesthetic, packaging must protect a product. This is its primary function. However, recycling, marketing, weight, and cost constraints are forcing us to replace certain materials (particularly rigid materials such as glass and metal) which perform this primary function. The most widespread solution today is to use barrier materials. These are particularly resistant materials that ensure that the products they contain are well preserved. In the form of a very thin membrane, the barrier material sticks to the main material chosen for the packaging (paper, cardboard, etc.) to meet a specific need. In particular, it protects against moisture and gas, something that paper alone cannot do. Think of the polymer film used to wrap bread or coffee.
While multilayer packaging solutions are the most widely used, it is also possible to treat materials directly to improve their own barrier properties (nanocomposites, scavengers, etc.).
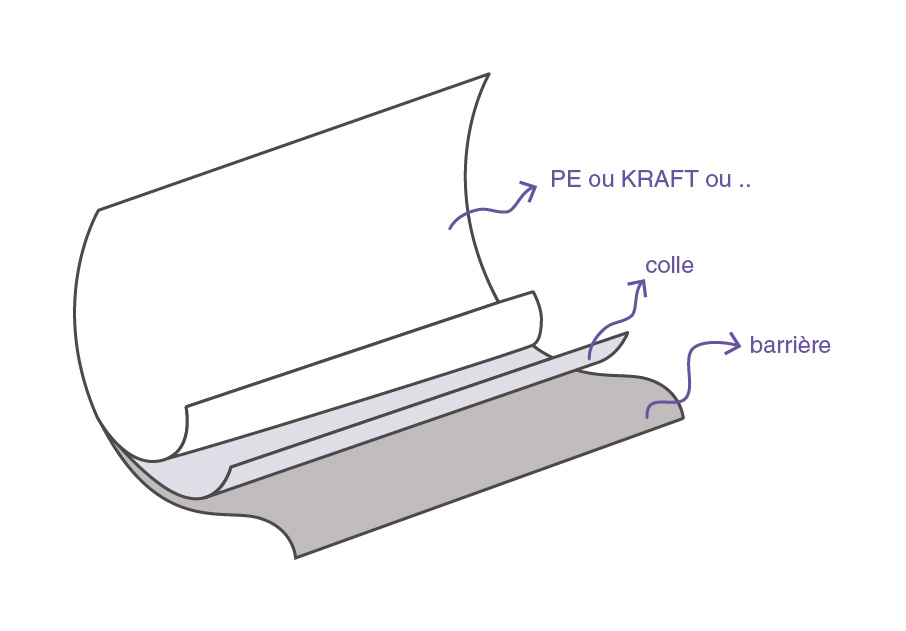
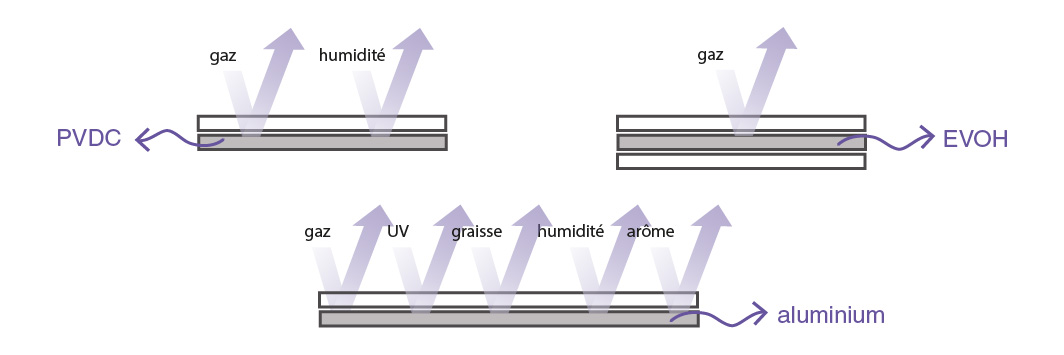
The different types of barrier materials
There are different barrier materials, which can be divided into two groups: polymers and metals. Each has its own advantages and disadvantages for your packaging. Here is a list of the main barrier materials :